Wordpress
An Example for a simple docker compose setup. To start a Wordpress application with a database and browser access.
Table of Contents
Description
A simple demo showing how docker compose works with multiple services.
Services included:
- WordPress #Application
- Mariadb #Database
- Adminer #Database GUI
Prerequisites
Repository Structure
wordpress_example/
├── docker-compose.yml # Docker container setup
├── img/ # All Images (Screenshots)
├── .env.example # All environment variables
├── .gitignore # Ignore rules for Git
├── README.md # Project overview and navigation
└── Wordpress_Checkliste.pdf # Checklist_DA
Quickstart
- Download the project:
git clone https://github.com/GeorgStrassberger/wordpress_example.git
- Navigate into the project folder
cd ./wordpress_example
- Create your .env file
cp .env.example .env
- Change the environment variables
# Copy this file to .env and fill in the values
# WordPress Example Environment Variables
WORDPRESS_DB_HOST=mariadb:3306
WORDPRESS_DB_NAME=wordpress
WORDPRESS_DB_USER=wp_user #Your Username
WORDPRESS_DB_PASSWORD=wp_pass #Your Password
# MariaDB Environment Variables
MYSQL_DATABASE=wordpress
MYSQL_USER=wp_user #Your Username
MYSQL_PASSWORD=wp_pass #Your Password
MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=root_pass #Your Root Password
- Pull Docker images and start the containers
docker compose up -d
docker compose: container groupup: Start all container-d: detached mode (runs in the background)
-
Open your browser to access WordPress on http://localhost:8080
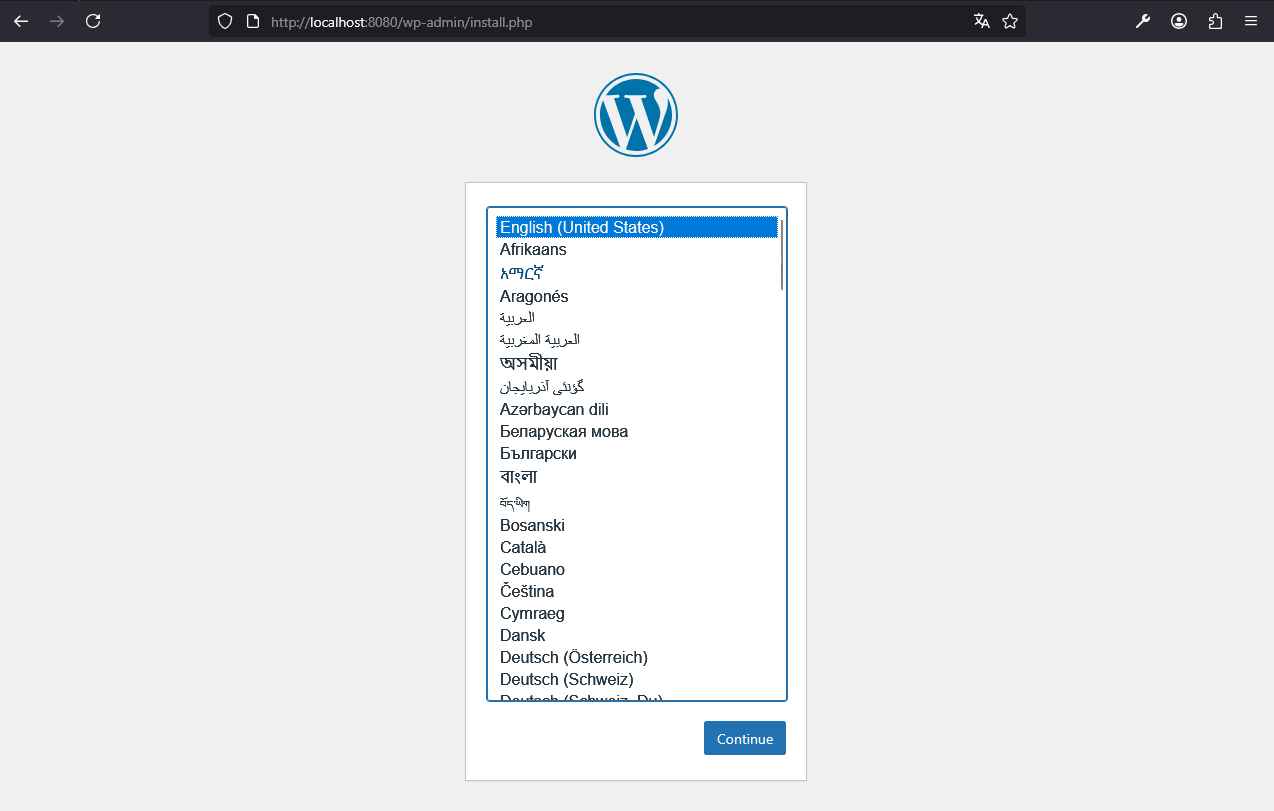
-
Open your browser to access Adminer on http://localhost:8081
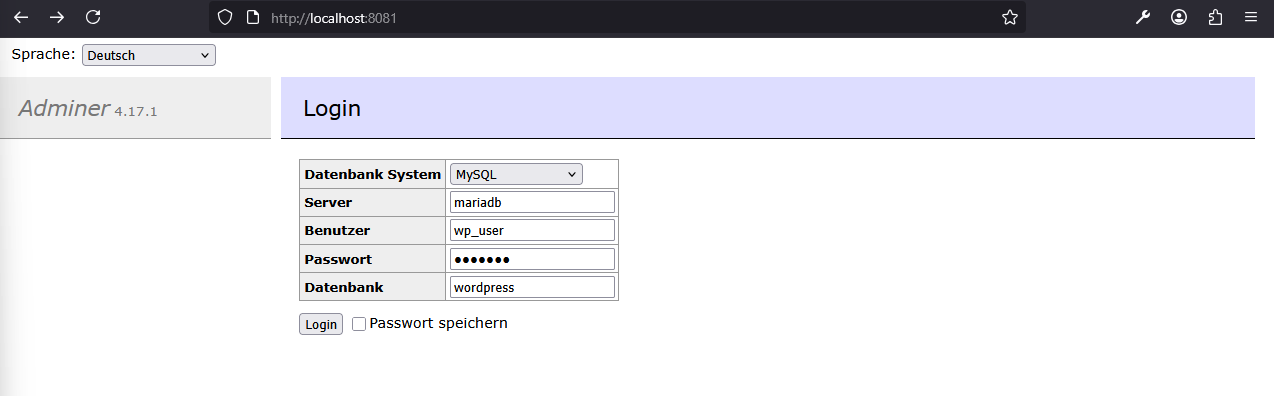
-
Adminer Login
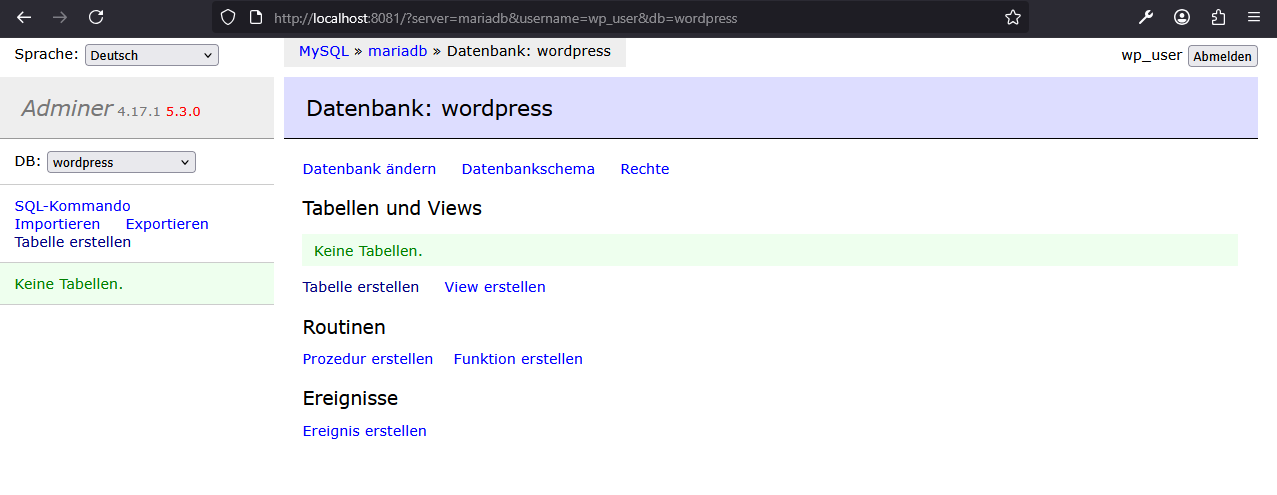
-
Stop and remove the containers and volumes
docker compose down -v
docker compose: container groupdown: stop and remove all containers-v: also remove volumes (data)
Usage
After starting the containers, you can:
- Access WordPress
- URL: http://localhost:8080
- Complete the initial WordPress setup wizard (choose site name, admin user, password)
- Access Adminer (Database GUI)
Normal User Login:
User-Login (user access):
System: MySQL #DB type
Server: mariadb #Docker service name of the database container
Username: wp_user #MYSQL_USER
Password: wp_pass #MYSQL_PASSWORD
Datenbank: wordpress #MYSQL_DATABASE
Root Login:
Root-Login (administrator access):
System: MySQL #DB type
Server: mariadb #Docker service name of the database container
Username: root #MYSQL_USER
Password: root_pass #MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD
Datenbank: (empty)
Author
██████╗ ███████╗ ███████╗ █████████╗
██╔════╝ ██╔════╝ ██╔═════╝ ╚══██╔═══╝
██║ ███╗ █████╗ ╚█████╗ ██║
██║ ██║ ██╔══╝ ╚═══██╗ ██║
██║ ██║ ██║ ██╗ ██║
╚██████╔╝ ███████╗ ███████║ ██║
╚═════╝ ╚══════╝ ╚══════╝ ╚═╝