Babyshop
Table of Contents
Overview
This repository serves as an example of how to use a Dockerfile to build a Docker image and subsequently create a container to host a Django-based project.
The project demonstrates:
- Building a custom Docker image for a Django application.
- Running the application in a Docker container.
- Hosting the application on a specified port accessible via the host system.
Prerequisites
To run this project, ensure you have the following installed on your system:
Quickstart
1. Clone the Project
git clone https://gitlab.com/geeser/baby_tool_shop.git
cd baby_tool_shop/babyshop_app
2. Build the Docker Image
docker build -t babyshop .
-t | tagThe -t option allows you to give the image an easily recognizable name and, optionally, a version (e.g., babyshop:1.0)..The dot (.) means the current directory is used as the build context.
Note Link to the Dockerfile with description.
3. Create Docker Volumes
To store the data persistently, so that it is not lost during a restart, we attach 2 volumes. In this case for the database und images.
docker volume create babyshop_db
docker volume create babyshop_media
4. Create a Docker Container from the Image
docker run -d \
-p 8025:8000 \
--name babyshop-app \
-v babyshop_db:/babyshop/db \
-v babyshop_media:/babyshop/media \
--restart unless-stopped \
babyshop
-d | detachedRuns the container in the background.-p | portMaps the container's internal port (5000) to a port on the host system (8025).--nameAssigns a custom name to the container.-v | VolumeMounts the data from the host system into the container.--restartConfigures the container's restart policy.alwaysThe container is always restarted, regardless of its exit status.unless-stoppedThe container is restarted unless it was manually stopped.on-failure[:n]The container is restarted only if it exits with a non-zero status (an error) Optionally, you can specify a limit on restart attempts (n).noThe container will not be restarted automatically (default behavior).
5. Log into the Container
docker exec -it babyshop-app bash
execAllows you to run commands directly inside a container without restarting it.-it | interactive & terminalThese options combined allow for an interactive shell session inside the container.babyshop-appThe name of the container where the command will be executed.bashStarts the container's Bash shell, allowing you to work directly within the container.
6. Create an Admin User
python manage.py createsuperuser
Username: admin
E-Mail-Adresse: admin@example.com
Passwort: *****
Passwort (nochmals): *****
7. Open the Admin Dashboard
Access the admin dashboard at: http://localhost:8025/admin
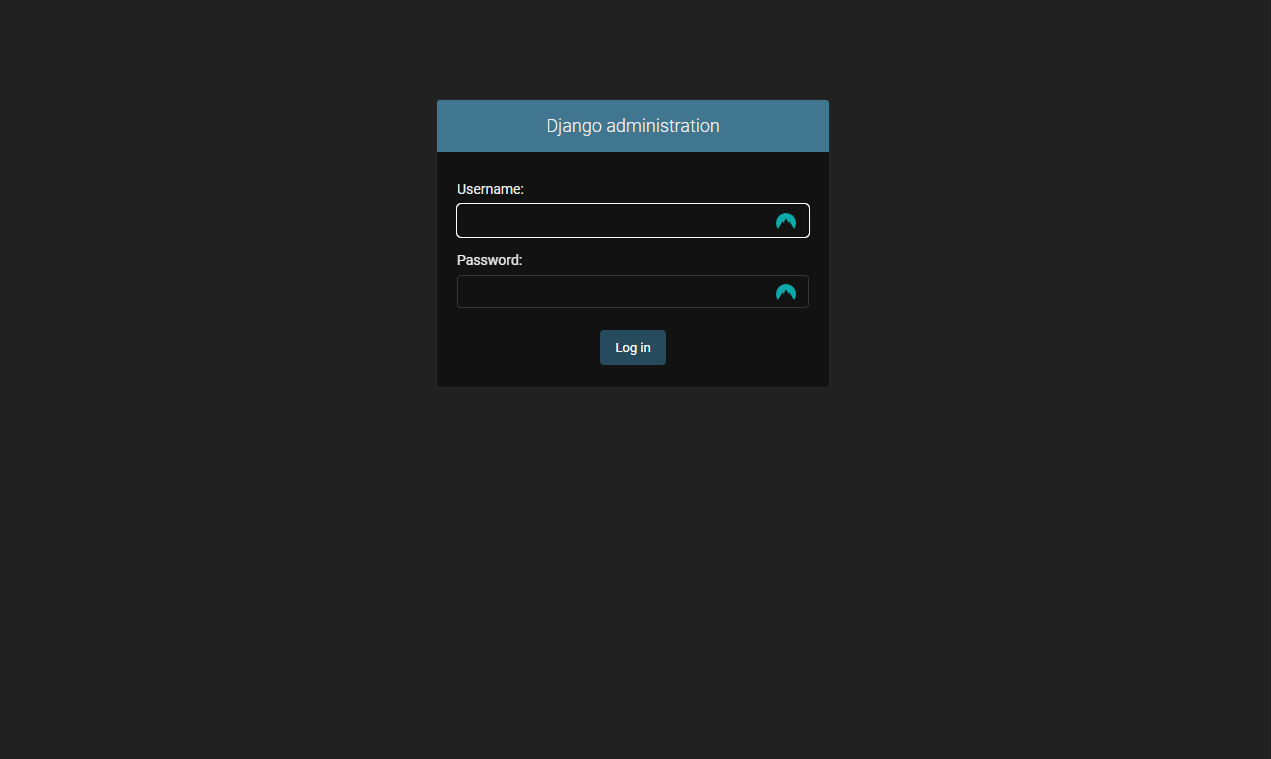
8. Add Content to the Application
Once logged in, add content to the application:
- Categorys
- Products
- Users
- Groups
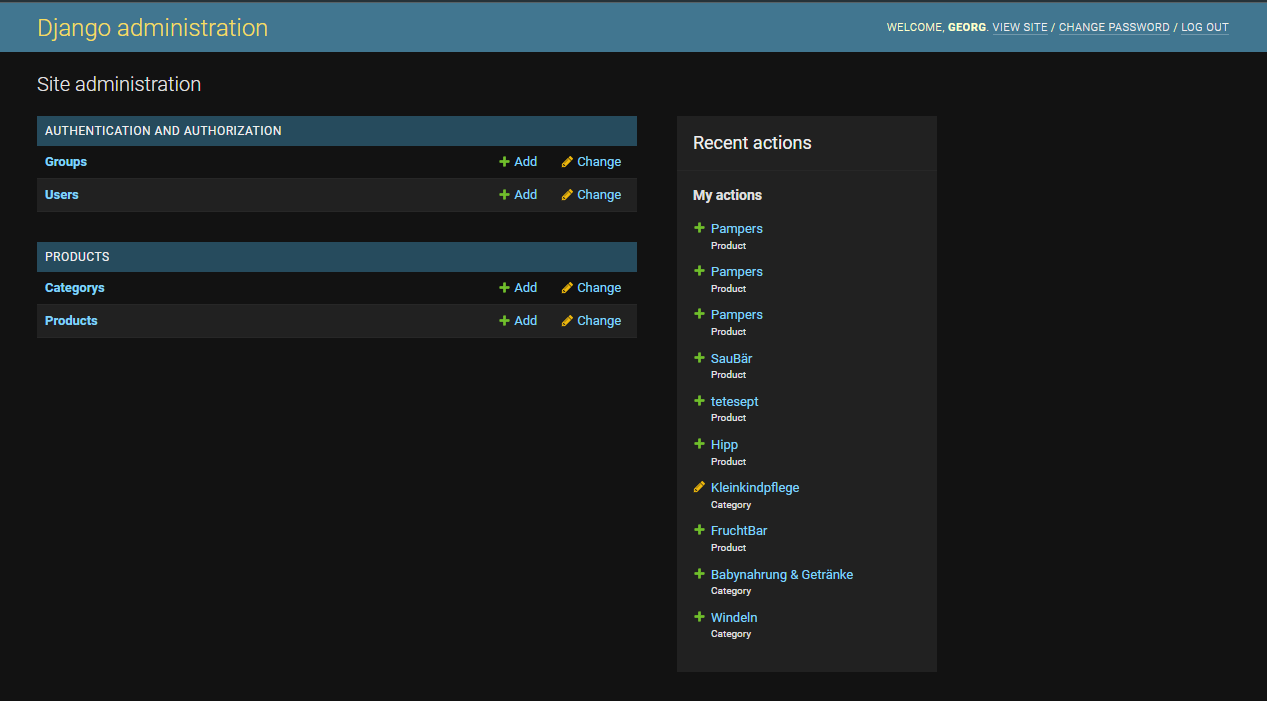
Preview
Below is a preview of the application running in the Docker container with content added: